Difference between revisions of "WCPS: Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator"
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
The interfaces between SLDRT and WSAN are socket connections between the PCs that run SLDRT and the Pis, and serial connections between the Pis and the end nodes. In this way, the end nodes of the sensing and actuation flows can be any nodes in the testbed. | The interfaces between SLDRT and WSAN are socket connections between the PCs that run SLDRT and the Pis, and serial connections between the Pis and the end nodes. In this way, the end nodes of the sensing and actuation flows can be any nodes in the testbed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == WCPS-EC == | ||
| + | |||
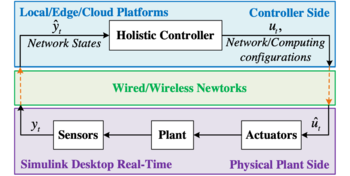
| + | [[File:Wcps_architecture_wcps_EC.png|350px|thumb|right|Figure 5. WCPS-EC Architecture]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We built a real-time hybrid simulator, wireless cyber-physical simulator edge-computing (WCPS-EC), which integrates (1) Real controllers running on various computation platforms; (2) Real Wi-Fi network and Ethernet, or simulated network using TOSSIM; (3) Simulink Desktop Real-time (SLDRT), which simulates robotic arm in real-time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The architecture of WCPS-EC is shown in Fig. 5. Compared with WCPS-RT, WCPS-EC includes immigrated controllers running on various computation platforms instead of controllers running in MATLAB/Simulink. In addition, WCPS-EC can reflect the impacts of real communication network and computation platform during run-time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In WCPS-RT, the worst-case end-to-end latency is below one sampling period. Hence the actuation commands are set to have fixed latency of one sampling period. However, in multi-tier control systems, the end-to-end latency can be longer than one sampling period. In addition, we consider a more realistic control system setup with (1) clock-driven sensors that sample the plant outputs periodically every sampling period; (2) an event-driven controller which calculates the actuation commands as soon as the sensor data arrives; and (3) event-driven actuators, which means actuators can respond to updated actuation commands immediately. | ||
== Talks == | == Talks == | ||
| + | *Y. Ma, C. Lu, B. Sinopoli and S. Zeng, [http://cps.cse.wustl.edu/index.php/File:EMSOFT.pdf Exploring Edge Computing for Multi-Tier Industrial Control], ESWEEK 2020 - ACM International Conference on Embedded Software (EMSOFT), September 2020. | ||
* Yehan Ma, [http://cps.cse.wustl.edu/index.php/File:ICII.pdf Efficient Holistic Control over Industrial Wireless Sensor Actuator Networks] , IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet (ICII'18), Seattle, October 23, 2018. | * Yehan Ma, [http://cps.cse.wustl.edu/index.php/File:ICII.pdf Efficient Holistic Control over Industrial Wireless Sensor Actuator Networks] , IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet (ICII'18), Seattle, October 23, 2018. | ||
* Chenyang Lu, [http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~lu/talks/iccps16.pdf Wireless Routing and Control: a Cyber-Physical Case Study] , ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'16), Vienna, April 11, 2016. | * Chenyang Lu, [http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~lu/talks/iccps16.pdf Wireless Routing and Control: a Cyber-Physical Case Study] , ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'16), Vienna, April 11, 2016. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:59, 23 November 2020
Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator (WCPS) is an open-source simulation environment for wireless control systems. By integrating Simulink and the TOSSIM wireless sensor simulator in a holistic simulation environment, WCPS accurately captures the dynamics of both the physical systems and the wireless sensor-actuator networks used for control. WCPS has been used for realistic case studies of wireless structural control systems for civil infrastructure, studying routing and control of cyber physical system, and incorporating emergency alarms in reliable wireless process control. The broad application of WCPS is to support cyber-physical systems research on large-scale wireless control systems through high-fidelity joint cyber and physical simulations. This site includes the code release, tutorial, and simulation examples for wireless structural control systems.
Contents
What's New
- [Software Release] WCPS-EC is released. here.
- [Software Release] WCPS-RT is released. here.
- [Software Release] Dockerized WCPS v3.0 for industrial process control is released. here.
- [Software Release] Benchmark Problem in Active Structural Control with Wireless Sensor Network.
- [Software Release] WCPS v2.0 is released.
- [Software Update] Benchmark Wireless Structural Control Problem, July 29, 2014.
- [News] Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges, August 07, 2013.
- [News] Washington Bridge Collapse Could Be a Wake-up Call, May 30, 2013.
- [News] Matthew Roblez: Structural Engineering Saves Lives, May 22, 2013.
- [News Release] Engineering Professor Working to Help Bridges Survive Natural Disaster, April 26, 2013.
- [Paper] Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control, ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), April 2013.
- [Software Update] A complete package of Cygwin with TinyOS 2.1.1, MLA, TOSSIM pre-installed was released here, April 01, 2013.
- [Software Update] WCPS v0.1.1 and the four cases studies for the ICCPS'13 paper was released here, March 10, 2013.
- [Tutorial] Wireless structural control examples from a structural perspective, March 09, 2013.
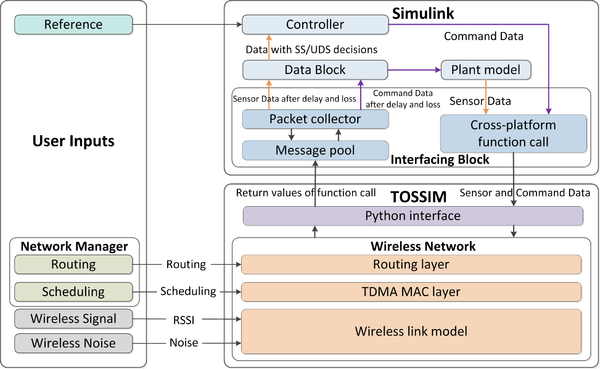
WCPS Architecture
In the Fig.1, WCPS simulates the feedback control loop of the control system as follows. Sensor data is generated from plant models such as structures and water tanks. Through a cross-platform function call from Simulink, sensor data is injected to the corresponding wireless sensors in TOSSIM. Following the routes and transmission schedule calculated by the network manager module, TOSSIM simulates the end-to-end wireless communication of the sensor data packets from the sensors to the base station, and then return the packet delay and loss to the Interfacing Block in Simulink through the Python interface. The Packet Collector module extracts packet delivery information(the delay and loss)from the message pool. Sensor data and their loss and delay are provided to the Data Block, which can feed the sensor data to the controller at the right time based on the packet delay (if the packet is not lost). WCPS utilizes basic API (e.g., the dos, UNIX command) of MATLAB to do cross-platform function calls. In TOSSIM, we re-implement a printf method in TinyOS to send simulation results to the Interfacing Block.
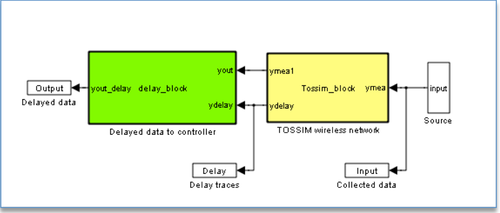
User inputs to WCPS includes reference signals of the plants and wireless traces used as input to TOSSIM. The scheduler module calculates transmission schedules. Networking schedule is then deployed into the MAC layer code of wireless nodes and becomes effective after a TinyOS compilation. The TDMA MAC layer in WCPS is developed based on the MAC Layer Architecture (MLA) library and further adapted for TOSSIM under TinyOS 2.1.1. Received Signal Strength Indication( RSSI) and wireless noises traces are collected from real-world environments and provided to the wireless model used by TOSSIM for realistic wireless network simulations. The interfaces between the Simulink model and TOSSIM are encapsulated as two MATLAB embedded functions in Simulink: the Interfacing Block and the Data Block, as is shown in Fig.2. The Interfacing Block extracts delay and loss information from TOSSIM messages, and the Data Block decides what data will be used for discrete control during each sampling period. The federated architecture of WCPS provides great flexibilities to incorporate different structural models and implement alternative scheduling-control approaches.
Environment Installation
- Install TinyOS
WCPS is implemented and tested on MacOS X (snowleopard), Windows XP, and Windows 7. Current release of WCPS is under TinyOS 2.1.1, which can be installed following the two methods.
- Follow the TinyOS official tutorial on installation of TinyOS for your specific platform: Link
- Directly download the pre-tested TinyOS 2.1.1 image from here: TinyOS2.1.1 for SnowLeopard(and possibly later versions) [Cygwin package coming soon.]
- Install Mac Layer Architecture(MLA)
The MAC Layer Architecture (MLA) provides a component-based architecture for MAC protocols in wireless sensor networks. MLA extends the Unified Power Management Architecture to provide the hardware-independent interfaces required by timing sensitive MAC protocols, and defines platform-independent reusable components that implement MAC layer logic on top of them. The MLA architecture can be used to develop a large number of platform-independent MAC implementations, with little or no further effort required to adapt these implementations to new hardware platforms. Our current implementation of MLA is built on top of TinyOS 2.1.1. It currently supports platforms which use the CC2420 radio stack and has been tested on TelosB motes. In addition to providing interfaces and components for building new MAC layer implementations, MLA includes implementations of five representative MAC layers. Specifically for WCPS, we adopt and further change the pure-TDMA MAC protocol for centralized data communication.
- Follow the instructions here: Install MLA.
- Install MATLAB and Simulink
- If you already have MATLAB MATLAB 7.11.0.584 (2010b) or later version, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the tutorial here: install MATLAB
- Install Python
If you already have Python 2.7.2 or later version installed, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the manual here: install Python
Below is the installation guide of WCPS v3.0. For Mac OSX Users who would like to run WCPS on their own computer, please follow first instruction link below for a detailed installation and test procedures. For OSX/Linux/UNIX/Windows users, please follow the second instruction link below for ruining Dockerized WCPS in a Docker container.
- Install WCPS v3.0 on Mac. Run_WCPS_On_Mac_Guide
- Run WCPS v3.0 using Docker Container. Run_WCPS_In_Docker_Container_Guide
Download WCPS
- Dockerized WCPSv3: Docker image, local Matlab folder.
- Local WCPSv3 installation folder.
- A complete package of Cygwin with TinyOS 2.1.1, MLA, TOSSIM pre-installed with a WCPS Cygwin Installation & Usage Tutorial
- WCPS v0.1.1 and four extensive case studies for ICCPS'13 paper
Use WCPS
Wireless network plays a critical role in close-loop wireless control system. Sitting on top of WCPS, simulating a wireless TDMA network is as easy as collecting these NesC files below:
- "Makefile" takes advantage of the fact that it's not necessary to recompile all the files not changed while specifying all necessary libraries.
- "TestNetwork.h" defines necessary message structures for the wireless communication.
- "TestNetworkAppC.nc" connects claimed application interfaces to interfaces that are defined in the hardware library.
- "TestNetworkC.nc" implements send/receive functionality of a wireless node.
- "tossim-call.py" configures TOSSIM network and does packet injection into the Tossim network.All above necessary files..
- Re-implemented TOSSIM libraries for TDMA simulation.TDMA components for TOSSIM..
- Wireless traces: Traces for 5-sensor wireless network in a building.
Put all the above files into the same folder, prompt a terminal (or a Cygwin window), and in the terminal run
Make micaz sim
If TinyOS and python is configured correctly, go ahead and run in the terminal:
./tossim-call.py
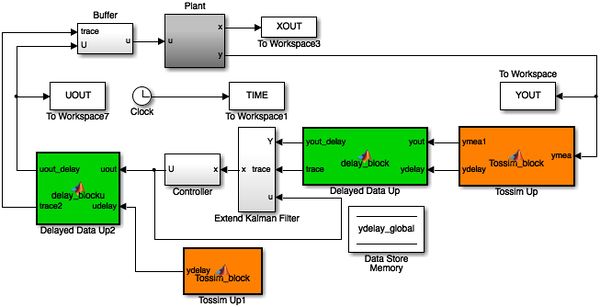
Having collected aforementioned TinyOS files, a simplified example that uses key networking Interfacing Block and Data Block of WCPS is shown in Fig. 3.
This examples shows:
- How input data in Simulink is injected to TOSSIM network;
- How TOSSIM Interfacing Block runs as a Matlab Embedded function;
- What type of data is output from the Interfacing Block;
- How data usage strategies are applied to the data in the Data Block.
- What type of data is eventually output from the Data Block and provided for future control use.
Source code for the example can be found here. To run this integrated example, simply download, unzip the source code, and run Run_delay_data_func.m in Matlab.
WCPS-RT
Given the complexity of wireless communication in physical environments, simulators cannot always capture the real-world behavior of WSANs. Network-in-the-loop simulations have been developed to address the limitation of wireless simulations by incorporating physical wireless networks.
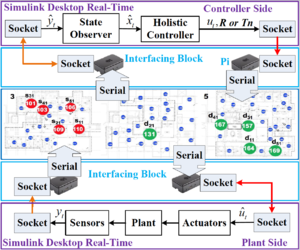
To experiment with wireless control over real-world WSANs, we develop wireless cyber-physical simulator real-time (WCPS-RT). WCPS-RT integrates MATLAB/Simulink Desktop Real-time (SLDRT) and a 3-floor WSAN testbed. It captures realistic wireless dynamics that are hard to simulate accurately, and leverages simulation support for controllers and physical plants. The architecture of WCPS-RT is shown in Fig. 4.
SLDRT is used to simulate the physical part of the WNCS: physical plants, controllers, state observers, and physical disturbance. In practice, industrial plants usually operate continuously or at very high rates. However, the wireless communication and controller execute at a relatively low rate because of the communication and computation latencies. Therefore, SLDRT modules are operated at different rates in our design.
The 3-floor WSAN testbed is deployed on the 3rd to 5th floors of Jolley Hall at Washington University in St. Louis. It consists of 70 TelosB motes. Each mote is equipped with Chipcon CC2420 radio compliant with the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and a TI MSP430 microcontroller. 40 Raspberry Pis with a backplane network are used for the management of the WSAN.
The interfaces between SLDRT and WSAN are socket connections between the PCs that run SLDRT and the Pis, and serial connections between the Pis and the end nodes. In this way, the end nodes of the sensing and actuation flows can be any nodes in the testbed.
WCPS-EC
We built a real-time hybrid simulator, wireless cyber-physical simulator edge-computing (WCPS-EC), which integrates (1) Real controllers running on various computation platforms; (2) Real Wi-Fi network and Ethernet, or simulated network using TOSSIM; (3) Simulink Desktop Real-time (SLDRT), which simulates robotic arm in real-time.
The architecture of WCPS-EC is shown in Fig. 5. Compared with WCPS-RT, WCPS-EC includes immigrated controllers running on various computation platforms instead of controllers running in MATLAB/Simulink. In addition, WCPS-EC can reflect the impacts of real communication network and computation platform during run-time.
In WCPS-RT, the worst-case end-to-end latency is below one sampling period. Hence the actuation commands are set to have fixed latency of one sampling period. However, in multi-tier control systems, the end-to-end latency can be longer than one sampling period. In addition, we consider a more realistic control system setup with (1) clock-driven sensors that sample the plant outputs periodically every sampling period; (2) an event-driven controller which calculates the actuation commands as soon as the sensor data arrives; and (3) event-driven actuators, which means actuators can respond to updated actuation commands immediately.
Talks
- Y. Ma, C. Lu, B. Sinopoli and S. Zeng, Exploring Edge Computing for Multi-Tier Industrial Control, ESWEEK 2020 - ACM International Conference on Embedded Software (EMSOFT), September 2020.
- Yehan Ma, Efficient Holistic Control over Industrial Wireless Sensor Actuator Networks , IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet (ICII'18), Seattle, October 23, 2018.
- Chenyang Lu, Wireless Routing and Control: a Cyber-Physical Case Study , ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'16), Vienna, April 11, 2016.
- Chenyang Lu, Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges, IEEE Spectrum, August 07, 2013.
- Chenyang Lu, Real-Time Wireless Control Networks for Cyber-Physical Systems, Computer Science Colloquium, Temple University, April 12, 2013.
- Bo Li, Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control, ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), Philadelphia, PA, April 11, 2013.
Publication
- Y. Ma, C. Lu, B. Sinopoli and S. Zeng, Exploring Edge Computing for Multi-Tier Industrial Control, IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (TCAD), Special Issue on ESWEEK 2020 - Proceedings of ACM International Conference on Embedded Software (EMSOFT), September 2020.
- Y. Ma, C. Lu and Y. Wang, Efficient Holistic Control: Self-Awareness across Controllers and Wireless Networks, ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems, Special Issue on Self-Awareness in Resource Constrained Cyber-Physical Systems, 4(4), Article 41, June 2020.
- Y. Ma and C. Lu, Efficient Holistic Control over Industrial Wireless Sensor-Actuator Networks, IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet (ICII'18), October 2018.
- Y. Ma, D. Gunatilaka, B. Li, H. Gonzalez and C. Lu, Holistic Cyber-Physical Management for Dependable Wireless Control Systems, ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems, Special Issue on Dependability in Cyber Physical Systems and Applications, 3(1), Article No. 3, August 2018.
- B. Li, Y. Ma, T. Westenbroek, C. Wu, H. Gonzalez, C. Lu. (2016, April). Wireless Routing and Control: a Cyber-Physical Case Study. ACM/IEEE 7th International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'16), April 2016.
- B. Li, L. Nie, C. Wu, H. Gonzalez, C. Lu.Incorporating Emergency Alarms in Reliable Wireless Process Control. ACM/IEEE 6th International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'15), April 2015.
- B. Li, Z. Sun, K. Mechitov, G. Hackmann, C. Lu, S. Dyke, G. Agha and B. Spencer, "Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control," ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), April 2013.
Get Support
- WCPS v3.0: Yehan Ma: yehan.ma@wustl.edu