Difference between revisions of "WCPS: Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Live Example == | == Live Example == | ||
| − | == | + | ===Installation=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | ==== Install TinyOS ==== |
| − | === Install TinyOS === | ||
WCPS is implemented and tested on MacOS X (snowleopard), Windows XP, and Windows 7. | WCPS is implemented and tested on MacOS X (snowleopard), Windows XP, and Windows 7. | ||
Current release of WCPS is under TinyOS 2.1.1, which can be installed following the three methods. | Current release of WCPS is under TinyOS 2.1.1, which can be installed following the three methods. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 17: | ||
*(2) Directly download the pre-tested TinyOS 2.1.1 image from here: [under construction Cygwin] [under construction Mac OS X] | *(2) Directly download the pre-tested TinyOS 2.1.1 image from here: [under construction Cygwin] [under construction Mac OS X] | ||
| − | === Install Mac Layer Architecture(MLA) === | + | ==== Install Mac Layer Architecture(MLA) ==== |
Follow the instructions here: [http://wsn.cse.wustl.edu/index.php?title=MAC_Layer_Architecture Install MLA]. | Follow the instructions here: [http://wsn.cse.wustl.edu/index.php?title=MAC_Layer_Architecture Install MLA]. | ||
| − | === Install MATLAB and Simulink === | + | ==== Install MATLAB and Simulink ==== |
If you already have MATLAB MATLAB 7.11.0.584 (2010b) or later version, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the | If you already have MATLAB MATLAB 7.11.0.584 (2010b) or later version, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the | ||
tutorial here: [http://www.mathworks.com/help/install/index.html install MATLAB] | tutorial here: [http://www.mathworks.com/help/install/index.html install MATLAB] | ||
| − | === Install Python === | + | ==== Install Python ==== |
If you already have Python 2.7.2 or later version installed, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the manual here: [http://www.python.org/getit/ install Python] | If you already have Python 2.7.2 or later version installed, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the manual here: [http://www.python.org/getit/ install Python] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 30: | ||
To test if TinyOS, Python and WCPS were configured correctly, pleas read ahead and do the following example. | To test if TinyOS, Python and WCPS were configured correctly, pleas read ahead and do the following example. | ||
| − | == Building a 5-node Network in TOSSIM == | + | === Building a 5-node Network in TOSSIM === |
| − | === Makefile === | + | ==== Makefile ==== |
"Makefile" takes advantage of the fact that it's not necessary to recompile all the project files that has not been changed. | "Makefile" takes advantage of the fact that it's not necessary to recompile all the project files that has not been changed. | ||
To have the "Makefile" for our project, copy the code below into a txt file and save as "Makefile" without any suffix. | To have the "Makefile" for our project, copy the code below into a txt file and save as "Makefile" without any suffix. | ||
| − | === TestNetwork.h === | + | ==== TestNetwork.h ==== |
"TestNetwork.h" defines necessary message structures for the wireless communication. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetwork.h". | "TestNetwork.h" defines necessary message structures for the wireless communication. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetwork.h". | ||
| − | === TestNetworkAppC.nc === | + | ==== TestNetworkAppC.nc ==== |
"TestNetworkAppC.nc" connects claimed application interfaces to interfaces that are defined in the hardware librare. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkAppC.nc". | "TestNetworkAppC.nc" connects claimed application interfaces to interfaces that are defined in the hardware librare. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkAppC.nc". | ||
| − | === TestNetworkC.nc === | + | ==== TestNetworkC.nc ==== |
"TestNetworkC.nc" Implements send/receive functionality of a wireless node. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkC.nc". | "TestNetworkC.nc" Implements send/receive functionality of a wireless node. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkC.nc". | ||
| − | === tossim-call.py === | + | ==== tossim-call.py ==== |
"tossim-call.py" configures TOSSIM network and does packet injection into the Tossim network. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "tossim-call.py". | "tossim-call.py" configures TOSSIM network and does packet injection into the Tossim network. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "tossim-call.py". | ||
| − | + | ==== Make ==== | |
| + | |||
| + | == Change Log == | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Get Support == | ||
Put all the above files into the same folder, prompt a terminal (or a Cygwin window), and: | Put all the above files into the same folder, prompt a terminal (or a Cygwin window), and: | ||
Revision as of 16:15, 14 March 2013
End-user's Tutorial on using WCPS: The Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator
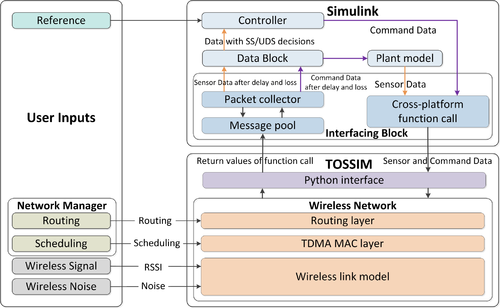
WCPS is design for, but not limited to, realistic Wireless Structural Control simulations. The efficient integration of Simulink and TOSSIM has made WCPS an ideal choice for realistic wireless control simulations. The following tutorial introduces how to install and configure MATLAB, TinyOS, and PYTHON environments, as well as the WCPS framework. The tutorial herein is specifically organized for end-users who do not do much development but instead trying to do wireless control simulations with Simulink and TOSSIM. A more advanced tutorial for developers can be found [here].
Contents
WCPS Principle
Live Example
Installation
Install TinyOS
WCPS is implemented and tested on MacOS X (snowleopard), Windows XP, and Windows 7.
Current release of WCPS is under TinyOS 2.1.1, which can be installed following the three methods.
- (1) Follow the TinyOS official tutorial on installation of TinyOS for your specific platform: Link
- (2) Directly download the pre-tested TinyOS 2.1.1 image from here: [under construction Cygwin] [under construction Mac OS X]
Install Mac Layer Architecture(MLA)
Follow the instructions here: Install MLA.
Install MATLAB and Simulink
If you already have MATLAB MATLAB 7.11.0.584 (2010b) or later version, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the tutorial here: install MATLAB
Install Python
If you already have Python 2.7.2 or later version installed, skip this step. Otherwise, follow the manual here: install Python
Environment Setup Testing
To test if TinyOS, Python and WCPS were configured correctly, pleas read ahead and do the following example.
Building a 5-node Network in TOSSIM
Makefile
"Makefile" takes advantage of the fact that it's not necessary to recompile all the project files that has not been changed. To have the "Makefile" for our project, copy the code below into a txt file and save as "Makefile" without any suffix.
TestNetwork.h
"TestNetwork.h" defines necessary message structures for the wireless communication. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetwork.h".
TestNetworkAppC.nc
"TestNetworkAppC.nc" connects claimed application interfaces to interfaces that are defined in the hardware librare. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkAppC.nc".
TestNetworkC.nc
"TestNetworkC.nc" Implements send/receive functionality of a wireless node. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "TestNetworkC.nc".
tossim-call.py
"tossim-call.py" configures TOSSIM network and does packet injection into the Tossim network. Copy the code below into a txt file and save as "tossim-call.py".
Make
Change Log
Get Support
Put all the above files into the same folder, prompt a terminal (or a Cygwin window), and: 1. In the terminal, Make micaz sim and hit return 2. In the terminal ./tossim-call.py
Wireless traces
To run the network simulation above, we need wireless RSSI (strength of the wireless communication signal) and wireless Noise for Tossim to build Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) model. Two options to do are:
1) Use the provided RSSI and noise traces for test purposes.
2) Use the code [rssi.zip] to collect the RSSI values and use code [noise.zip] to collect the wireless noise traces.
Test run
And you are ready to go for the wireless network setup.
Integrated Simulation with WCPS
Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control WCPS Software Version 0.1. WSC Examples from a structural perspective.
References
- B. Li, Z. Sun, K. Mechitov, G. Hackmann, C. Lu, S. Dyke, G. Agha and B. Spencer, "Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control," ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), April 2013.
- Z. Sun, B. Li, D. Dyke, and C. Lu. "A novel data utilization and control strategy for wireless structural control systems with tdma network," In Proc. ASCE IWCCE 2013.
- Z. Sun, B. Li, S.J. Dyke and C. Lu, "Evaluation of Performances of Structural Control Benchmark Problem with Time Delays from Wireless Sensor Network," Joint Conference of the Engineering Mechanics Institute and ASCE Joint Specialty Conference on Probabilistic Mechanics and Structural Reliability (EMI/PMC'12), June 2012.
- H. Lee, A. Cerpa, and P. Levis. Improving wireless simulation through noise modeling. In IPSN, 2007.
- P. Levis, N. Lee, M. Welsh, and D. Culler. Tossim: Accurate and scalable simulation of entire tinyos applications. In Sensys, 2003.
Contact us
- TinyOS and TOSSIM: Bo Li: boli@seas.wustl.edu
- Simulink Models: Zhuoxiong Sun: SUN152@purdue.edu