Difference between revisions of "Cyber-Physical Co-Design of Wireless Monitoring and Control for Civil Infrastructure"
(→Talks) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== What's New == | == What's New == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''[Software Release]''' [https://nees.org/groups/wireless_control_benchmark Benchmark Problem in Active Structural Control with Wireless Sensor Network]. | ||
* '''[News]''' [http://spectrum.ieee.org/podcast/at-work/test-and-measurement/smart-bridges Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges] [8/07/2013] | * '''[News]''' [http://spectrum.ieee.org/podcast/at-work/test-and-measurement/smart-bridges Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges] [8/07/2013] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:34, 13 July 2015
Supported by NSF through the Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Program
What's New
- [Software Release] Benchmark Problem in Active Structural Control with Wireless Sensor Network.
- [News] Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges [8/07/2013]
- [News] Washington Bridge Collapse Could Be a Wake-up Call [5/30/2013]
- [News] Matthew Roblez: Structural Engineering Saves Lives [5/22/2013]
- [News Release] Engineering Professor Working to Help Bridges Survive Natural Disaster [4/26/2013]
- [Paper] Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control, ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13) [4/2013]
- [Software Release] WCPS: Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator [3/2013]
Introduction
The objective of this research is to develop wireless distributed monitoring and control systems to enhance the resiliency of our civil infrastructure. We employ a cyber-physical co-design approach that integrates wireless sensor-actuator networks and structural monitoring and control algorithms. The unified cyber-physical system architecture and abstractions employ reusable middleware services to develop hierarchical structural monitoring and control systems.
The intellectual merit of this multi-disciplinary research includes:
- A unified middleware architecture and abstractions for hierarchical sensing and control;
- A reusable middleware service library for hierarchical structural monitoring and control;
- Customizable time synchronization and synchronized sensing routines;
- A holistic energy management scheme that maps structural monitoring and control onto a distributed wireless sensor-actuator architecture;
- Dynamic sensor and actuator activation strategies to optimize for the requirements of monitoring, computing, and control;
- Deployment and empirical validation of structural health monitoring and control systems on representative lab structures and in-service multi-span bridges.
While the system constitutes a case study, it will enable the development of general principles that would be applicable to a broad range of engineering cyber-physical systems.
This research will result in a reduction in the lifecycle costs and risks related to our civil infrastructure. The multi-disciplinary team is disseminating results throughout the international research community through open-source software and sensor board hardware as well as international summer schools and workshops.
Team
Faculty
- Chenyang Lu (Washington University)
- Gul Agha, Bill Spencer (UIUC)
- Shirley Dyke (Purdue University)
Members
- Greg Hackmann, Bo Li (Washington University)
- Kirill Mechitov, Parya Moinzadeh, Lauren Linderman (UIUC)
- Sriram Krishnan, Zhuoxiong Sun (Purdue University)
Ongoing Efforts
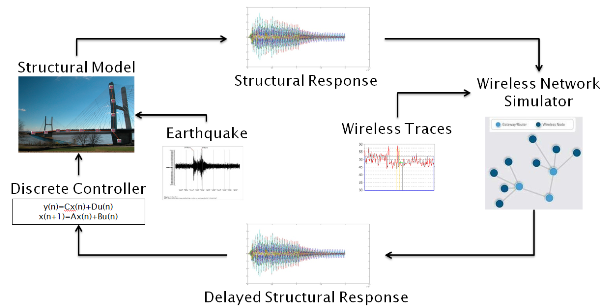
Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator (WCPS)
- A cyber-physical simulation framework combining state-of-the-art structural models and wireless networking simulation;
- Open source software released at [1];
- Enables realistic design and testing of wireless control systems;
- Case studies on wireless structural control for a building and a bridge;
- Representative paper: Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control, ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), April 2013.
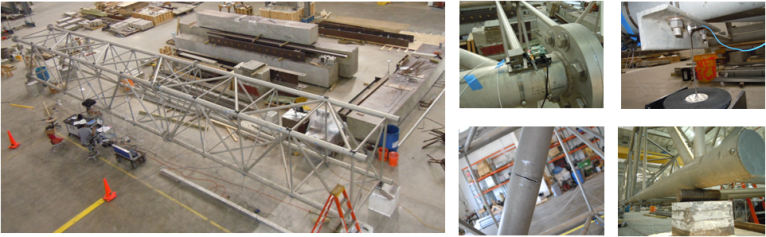
Full Scale Truss Experiment on Distributed Damage Localization
- Wireless sensors running distributed, multi-level damage detection deployed on a full scale truss (17.04m L × 1.83m W × 1.98m H) at Purdue;
- Damage detection results reflect actual damage locations, matching results from simulation.
- Representative paper: Cyber-Physical Codesign of Distributed Structural Health Monitoring with Wireless Sensor Networks, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, accepted.
Jindo Bridge Monitoring
- Field validation of wireless sensor-based monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge in Korea;
- Long-term autonomous monitoring using 113 wireless smart sensors;
- Establishment of an international testbed.
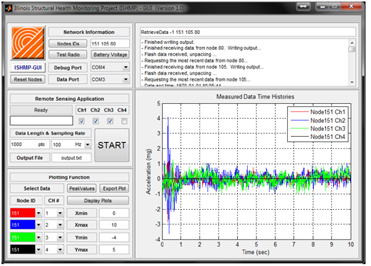
Monitoring Services Toolsuite
- Modular, service-oriented software library for assembling scalable monitoring applications;
- Core services: universal sensing, time synchronization, reliable communication, multi-hop routing, power management, numerical library;
- Used by 75 groups in 15 countries.
Software
WCPS: Wireless Cyber-Physical Simulator
- See the WCPS page for the software release, tutorial and existing case studies.
Decentralized Damage Localization based on the DLAC Method
- Source Code
- Installation Instructions
- Usage Instructions
- Paper: A Holistic Approach to Decentralized Structural Damage Localization Using Wireless Sensor Networks, IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS'08), December 2008.
Illinois SHM Services Toolsuite
Talks
- Chenyang Lu, Smart Bridges - Interview and Podcast on Cyber-Physical Systems for Resilient Bridges, IEEE Spectrum, August 07, 2013.
- Chenyang Lu, Real-Time Wireless Control Networks for Cyber-Physical Systems, Computer Science Colloquium, Temple University, April 12, 2013.
- Bo Li, Realistic Case Studies of Wireless Structural Control, ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS'13), Philadelphia, PA, April 11, 2013.
- Chenyang Lu, Real-Time Wireless Control Networks: Challenges and Directions, The NITRD National Workshop on The New Clockwork for Time-Critical Systems, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, October 25-27, 2012.
- Chenyang Lu, Cyber-Physical Co-Design for Wireless Structural Health Monitoring, Distinguished Lecture, University of Louisville, Nov. 2011.
- Chenyang Lu, My (biased) Perspective on CPS, Panel on Networked Monitoring and Control/Cyber-Physical Systems, Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems (ECRTS'11), Porto, Portugal, July 2011.
- Greg Hackmann, "Cyber-Physical Codesign of Distributed Structural Health Monitoring With Wireless Sensor Networks", ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS), April 2010. [PPTX] [PDF]
- Chenyang Lu, Distributed Structural Health Monitoring, CONet Joint Seminar, Swedish Institute of Computer Science (SICS), Stockholm, Sweden, July 2009.
- Greg Hackmann, "A Holistic Approach to Decentralized Structural Damage Localization Using Wireless Sensor Networks", IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS), December 2008. [PPTX] [PDF]